Vim CheatSheet
- id: 1692266403
- Date: Aug. 1, 2025, 12:50 p.m.
- Author: Donald F. Elger
NVimTree
- nvim plugin for file management
<leader-E>| Toggle tree on/off; key mappingg?| List key mappings:NVimTreeOpen <path>| Open to path
Nomenclature
- Buffers: In-memory text of files.
- Windows: Viewports onto buffers.
- Tabs: Collections of windows.
- Sessions: Saved states of your Vim environment.
- Marks: Saved positions in files.
- Registers: Storage for text and commands.
- Macros: Recorded sequences of commands.
- Folds: Collapsed sections of text.
- Quickfix List: List of locations for navigation.
- Location List: Window-specific list of locations.
- Autocommand: A command that automatically executes when a specific event occurs.
- Key Binding: An assignment of one or more commands to a key or key combination.
- Motion: What you want a command to operate on; word, sentence, paragraph, half-page, full-page, … # Delete
<C-w>| Delete word to left of cursor in insert mode.
Move
- Moving up:
k, <C-u>, <C-b>, gg - Moving down:
j, <C-d>, <C-f>, G - Moving right or right and down:
l, , $, ), }
Search
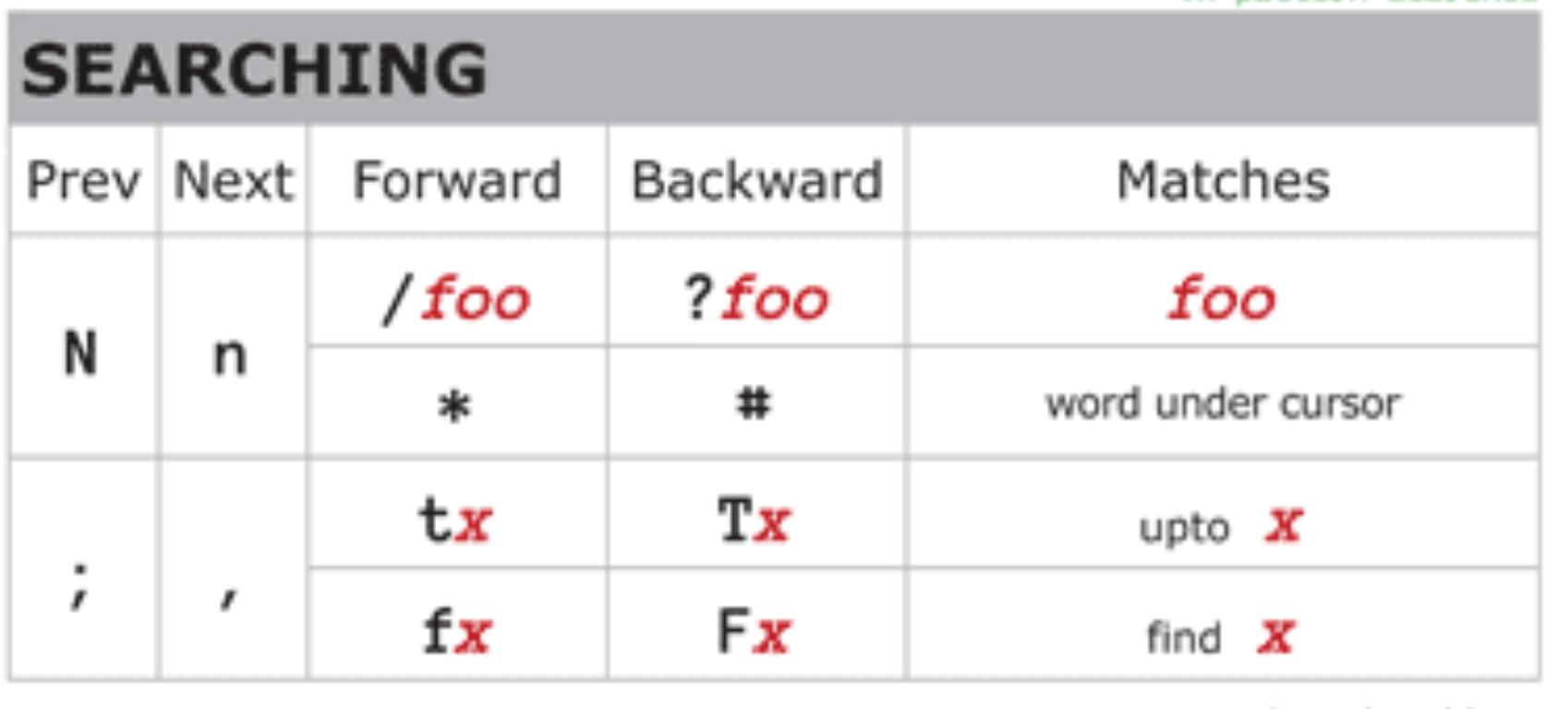 -
forward, back, next, previous
-
forward, back, next, previous
Getting Started
- Neovim configuration files (Mac)
~/.config/nvim/init.lua~/.config/nvim/init.vim
Edit
ct<x>= change to character but leave the charactercf<x>= change to character and delete the character
Search and Replace
:s/old/new/: generic syntax:%s/old/new/g%: Apply to entire fileg: replace all occurrences in a linec: prompt for confirmationi: ignore case
:5,10s/old/new/g: line range
User Interface
colo[scheme] <tab>| show list of colorschemes- To add a new scheme, placing them in your
~/.vim/colors/directory; then select with:colo sname cmd += toggle font size upward
Text
Set Configuration
$MYVIMRC= Environmental variable that holds the path to the init file~/.config/nvim/init.vim= Path name of init file:so[urce] ~/.config/nvim/init.vim= Source the init file
Move Cursor
Most Used Movements
hjkl: Move left, down, up, right for eachw: Move to the beginning of the next wordb: Move to the beginning of the previous worde: Move to the end of the current word0or^: Move to the beginning of the line$: Move to the end of the line
Screen Movements
H: Move to the top of the screenM: Move to the middle of the screenL: Move to the bottom of the screen
Page Movements
Ctrl + u: Move half a page up; scroll so this line is at bottom of the screenCtrl + d: Move half a page down; scroll so this line is as the top of the pageCtrl + b: Move one page upCtrl + f: Move one page down
Jumping
gg: Move to the beginning of the fileG: Move to the end of the file:<line_number>or<line_number>gg: Move to a specific line number
Miscellaneous
*: Move to the next occurrence of the word under the cursor#: Move to the previous occurrence of the word under the cursor%: Move to the matching parenthesis/bracket
Marks (Jump to a previously set mark)
m<letter>: Set a mark at the current cursor position<letter>: Jump to the mark named<letter>
Movements to characters
f': Move to the character; eg.f Jmoves to the nextJ`t: Move to just before character- ‘T’ and ‘F’ = Backwards character find
;: Repeat the last f, t, F, or T movement,: Repeat the last f, t, F, or T movement in the opposite direction
Searching
/<pattern>: Search forward for<pattern>?<pattern>: Search backward for<pattern>n: Move to the next search resultN: Move to the previous search result
Exiting Visual Mode / Cancelling
Esc: Exit visual mode or cancel an operation
More Help
:helporF1: Open Vim’s help documentation
Tabs
:tabe=:tabnew:tabn=:tabnext:tabp=:tabprevious:tabc=:tabclose:tabo=:tabonly:tabm=:tabmove:tabfir=:tabfirst:tabl=:tablast- Next
Tab:
gtor:tabn - Previous
Tab:
gTor:tabp - New Tab:
:tabe - Close Tab:
:tabc - Move Tab:
:tabm <N> - List Tabs:
:tabs
Windows
Move Windows Around
- precede windows commands with
<ctrl w> - x = exchange window with the next one
- H, J, K, L = move current window to be at the left, bottom top and right and make full size.
- r, R = rotate windows downwards/rightwards or opposite
Change Window Size
- Precede with windows commands
- Use an = to make windows all the same size
- <, > = decrease or increase window width
- -, + = decrease or increase window by
10 Ctrl-w += increase the height of the current window by 10 rows:resize 40= set the current window to 40 rows
Open New Windows
:new= Open a new horizontal windon:sp=:sp <path>= New horizontal windowvsp=vsp <path>= New vertical window
Spelling
<c-L>= in insert mode, automatically correct the mispelled word to the left of the insert pointz== suggest a word for the misspelled word under the cursor.- zg = add the word under the cursor to the spellfile
]s or [s= move forward/back to next misspelled word
Completions
- Completions List: Up/Down
- ↑ ↓
- Ctrl + n / Ctrl + p
- Tab / Shift + Tab: (Sometimes)
- Selecting a completion
<Enter>: Accept<C-Y>: Accept<C-e>: Cancel- Use mouse: if mouse support is enabled; enable it with
:set mouse=a
- Ignoring a completion: space, tab,
<esc>
Neovim Terminal Emulator
- Terminal Mode: The terminal window behaves like a regular shell.
- Normal Mode: The terminal window behaves like a vim window
<C-\><C-n>= Switch from terminal to normal modeiora= Switch from normal to terminal mode:term= Open terminal in a new buffer:split | term= Open terminal in a horizontal split:vsplit | term= Open terminal in a vertical split- Yank from Terminal: While in Normal mode, yank as
you would in any other buffer (e.g.,
yyto yank a line). - Paste to Terminal: In terminal mode, you can paste
using the normal paste shortcut for your shell. In Neovim’s terminal
mode, you can also use
Ctrl-W " p(assuming"is the desired register). - Close Terminal:
:q(while in Normal mode) or you can exit the terminal process, usually withexitorCtrl-d. - Set up terminal in ~/.config/nvim
Move/Copy Lines
[range]m[ove] {address}= Move lines[range]co[py] {address}= Copy lines- note: in older versions of vim, t is a alias for copy this no longer works in vim 9
Settings
- set ts=4 sw=4 ==> set the tabstop to 4 and the shiftwidth to 4
- set fo=tqn = set formatoptions to tqn
- :help formatoptions
- :set all = see all the format option; produces long list
- :set ma = set modifiable = allow the file to be edited
- :set noma = set nomodifiable = prevent file from being
- :help fo-table = see the meaning of the format option symbols
:set formatoptions+=t= add t to the format option list:help formatoptions
Format Options
- c = autowrap comments inserting the current symbol automatically; don’t like usually
- t = autowrap using textwidth
- q = Allow formatting of comments with “gq”
- o = continue comments with o or O
- r = continue comments with Enter
- autocmd FileType markdown setlocal formatoptions+=ro
- set fo+=ro
Folding
zf{motion} or {Visual}zf #Operator to create a fold.
zf’a # fold to mark
zF = Create a fold for N lines.
zd = Delete one fold at the cursor.
zD = Delete folds recursively at the cursor.
zE = Eliminate all folds in the window.
zo = Open one fold.
zO = Open all folds recursively.
zc = Close one fold.
zC = Close all folds recursively.
za = When on a closed fold: open it.and vice-versa.
zA = When on a closed fold: open it recursively.and vice-versa.
zR = Open all folds.
zM = Close all folds:
zn = Fold none: reset ‘foldenable’. All folds will be open.
zN = Fold normal: set ‘foldenable’. All folds will be as they were before.
zi = Invert ‘foldenable’.
[z = Move to the start of the current open fold.
]z = Move to the end of the current open fold.
zj = Move downwards. to the start of the next fold.
zk = Move upwards to the end of the previous fold.
Buffers
:ls=<c-l>(mapping) = list buffers<c-^>=<c-6>= switch back to buffer just edited from normal mode:bn=:bnext
:badd: buffer add :ls: list buffer buffer indicators: %: buffer in current window a: active buffer # alternate buffer, which can be accessed by Ctrl-6 : no indicator means that buffer is not loaded yet :bp: load previous buffer into current window :bn: load next buffer into current window :b2: load buffer No. 2 into current window :br: rewind first buffer into current window :bl: load last buffer into current window :ba: open all buffers into different windows :bd: delete buffer, take buffer number as arguments, :bd 1 2 3
Move Windows
Rotate windows
Reposition a window
& Move current window to far right \ <c-w> H
& Move to far left \ <c-w> J & Move to very
bottom \ <c-w> K & Move to very top \
\end{tabular}
Path Parts
:let @* = expand("%:p")= Copy full path to the clipboard:put =expand('%:p')= Copy full path into the buffer:echom expand("%:p")= Show full path on the command line
!:echo @%! & Show relative path on command line \ !@! & The @ symbol is used to prefix a register \ !%:e! & file extension \ !%:r! & full path less the extension \
:help expand
Search
*| Search forward for word under cursor
Settings
Automatic Formatting
Meaning: Format text automatically in paragraphs. Makes lists look greats. Makes c
Quitting
ZZin normal mode = Save current file if modified and exit; same as:x.:wq= Writes the file and then quits.ZQ=:q!= Exit unconditionally
Sessions
:mksession pn= save current session to pn (pathname)source pnread session saved at pn (pathname)
Surround
- Vim Surround is a plugin by Tim Pope that adds, change, or delete surrounding characters
:help surroundys<motion><surrounding>: Add a new surrounding text. For example,ysiw"adds double quotes around the current word.cs<old><new>: Change the surrounding text. For example,cs"'changes single quotes to double quotes.ds<surrounding>: Delete the surrounding text. For example,ds(removes surrounding parentheses.S<surrounding>: Add new surrounding to selected text. E.g. S* adds stars around the selected text.S[(: Add brackets around the current line.ys<text-object><surrounding>: Use text objects likeiw(inner word),i"(inner quotes),ap(a paragraph), etc.yss<surrounding>: Surround the entire line.yS<surrounding>: Surround with whitespace. For example,ySipsurrounds a paragraph with an extra space.ySs<surrounding>: Surround the line without whitespace.ySS<surrounding>: Surround the entire buffer.
Marks
- A mark is a marked position in a buffer that can be jumped to or referenced.
ma= set mark a at the current cursor position'a= jump to line of mark a\a` = jump to exact position of mark ad'a= delete from current line through line of mark a:marks= list current marks
Terminal
:term= Open a new horizontal terminal window:vert term= Open a new vertical terminal<c-d>= Close a terminal window<c-w>N= Toggle so you can move cursor around in window
Syntax Highlighting
:hi[ghlight]= List current highlight groups- :hi String ctermfg=1 guifg=#ff0000 | Change the string highlight color to red for both the terminal and the GUI
autocmd FileType python hi String ctermfg=1 guifg=#ff0000Add this to.vimrcto make this color change permanent.- Terminal Color Codes: 0-Black, 1-Red, 2-Green, 3 - Yellow 4 - Blue 5 - Magenta 6 - Cyan 7 - White 8 - Bright Black (Gray) 9 - Bright Red 10 - Bright Green 11 - Bright Yellow 12 - Bright Blue 13 - Bright Magenta 14 - Bright Cyan 15 - Bright White
General Syntax Highlighting:
:syntax enable- Enable syntax highlighting.:syntax off- Disable syntax highlighting.
Highlight Groups:
:hi GroupName- Show current highlighting settings for the specified group.:hi GroupName ctermfg=ColorNumber guifg=#HexColor- Change foreground color for the group.:hi GroupName ctermbg=ColorNumber guibg=#HexColor- Change background color for the group.:hi clear- Clear all highlighting settings.
Example Highlight Groups:
Normal- The default text color.Comment- Comments in code.String- Strings (single-quoted, double-quoted, triple-quoted).Keyword- Programming language keywords.Function- Function names.Type- Type names (class names, data types).
Filetype-Specific Highlighting:
autocmd FileType FileType hi GroupName ctermfg=ColorNumber guifg=#HexColor- Apply highlighting settings for a specific filetype.- Example:
autocmd FileType python hi Comment ctermfg=2 guifg=#00ff00(for Python comments).
Colors:
ctermfg=ColorNumber- Set foreground color using terminal color number (0-255).ctermbg=ColorNumber- Set background color using terminal color number (0-255).guifg=#HexColor- Set foreground color using hex color code.guibg=#HexColor- Set background color using hex color code.
Color Codes:
:help cterm-colors- Show a list of terminal color numbers.:help gui-colors- Show a list of GUI color names.
Scripts
:scriptnames=:scr= list all scripts, including plugins, that have been sourced in the order in which they were called.:set runtimepath?= list the path of plugins