Compare and Contrast
- id: 1702723261
- Date: Sept. 2, 2025, 10:49 a.m.
- Author: Donald F. Elger
Goals
- Describe compare and contrast.
- Apply this skill
What
Compare and contrast is the process of identifying both similarities and differences between two or more related but distinct things in order to better understand them.
Analysis: {process + similarities + difference + two or more similar items + seeking better understanding}
We can compare and contrast many things. Here are some examples.
- Apples and oranges.
- Mass and weight.
- Criminal law and civil law.
- Functional training and typical strength training.
- iPhones and Android phones.
- Manager candidate one versus manager candidate two.
- Critical Thinking versus Natural Thinking.
- Solar Power and Wind Power.
How
The Method
While quality is developing, take the following actions:
Selection: Choose the entities to be compared.
Research: Get good information about the two entities. Good info
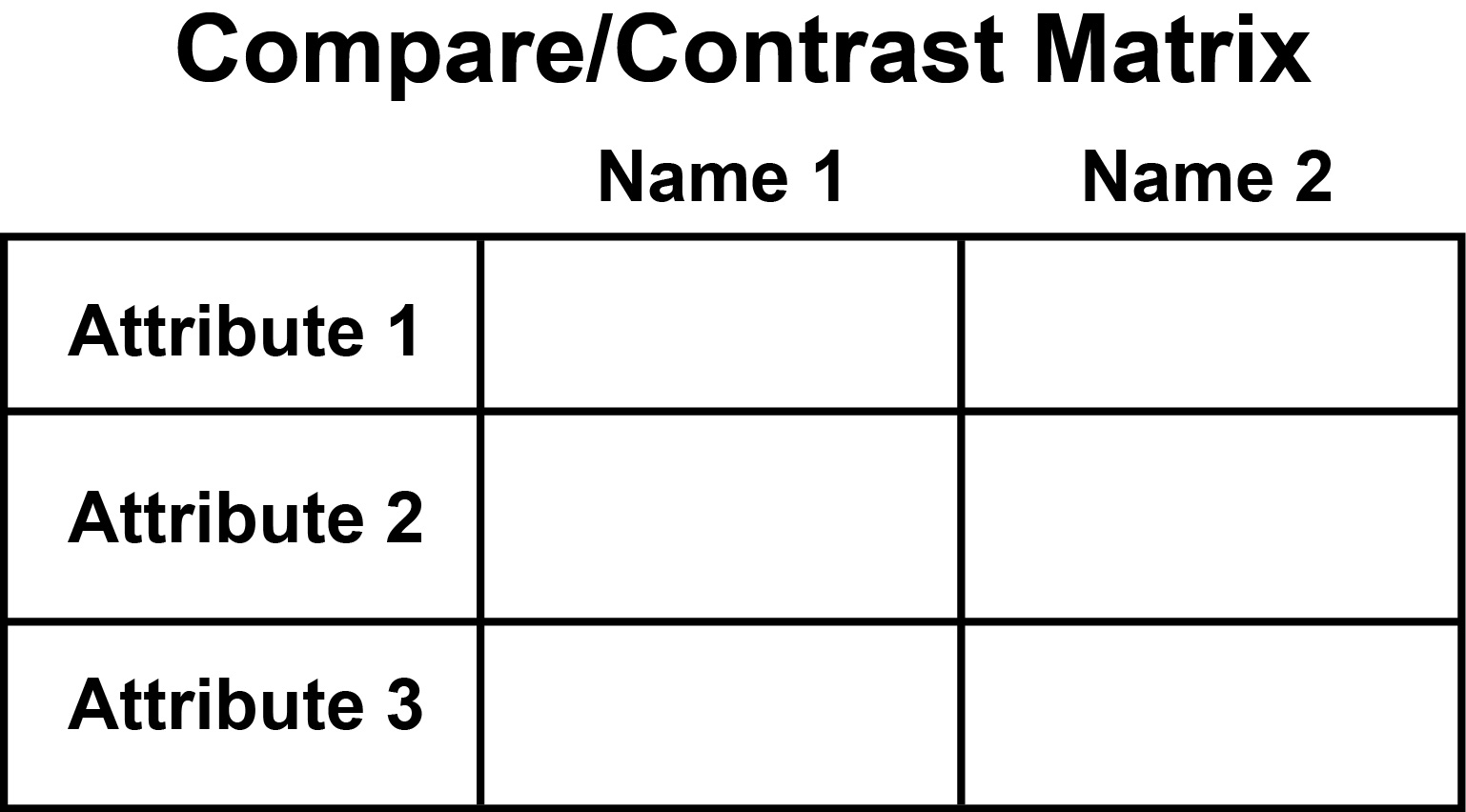
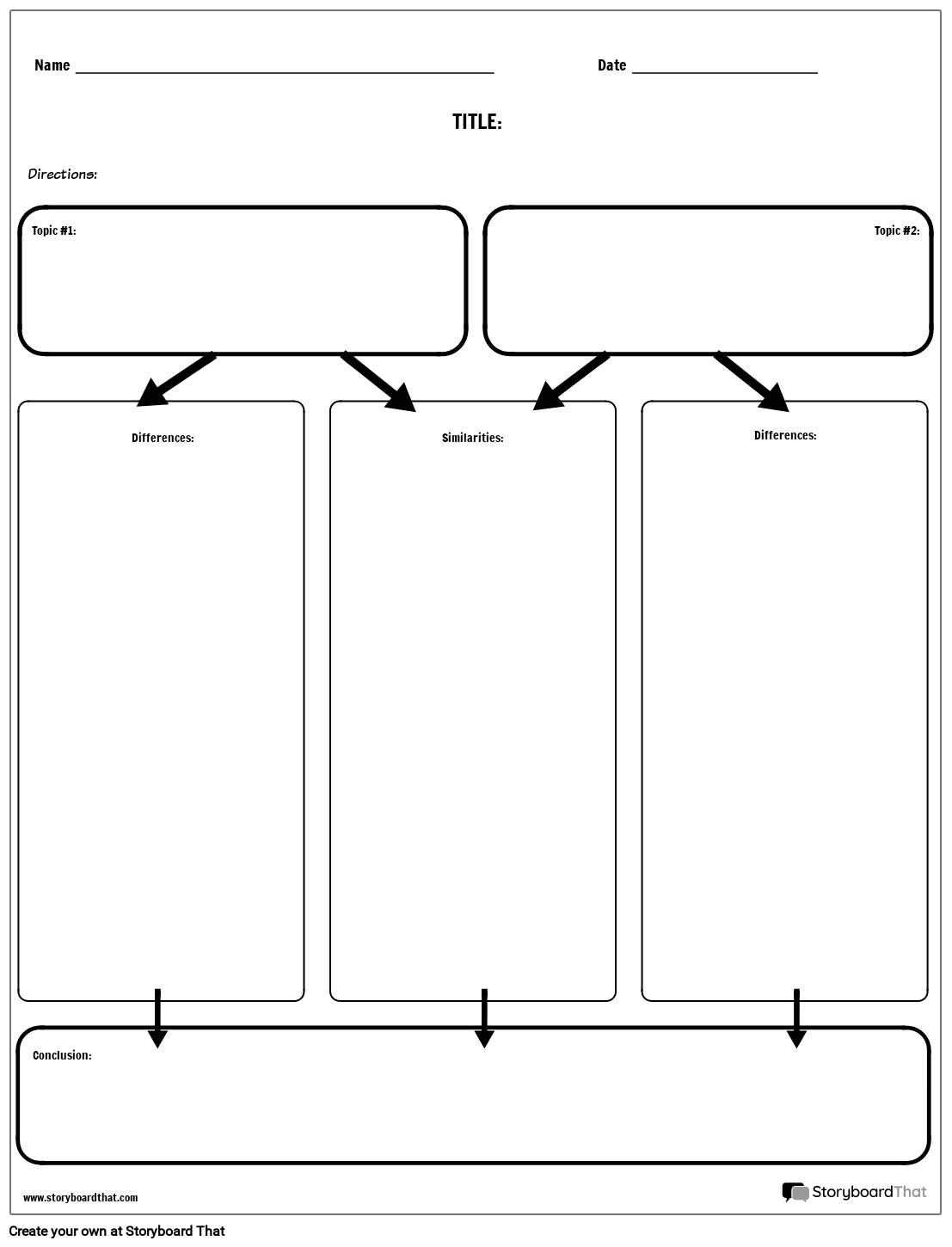
Presentation: Organize your results with the best structure: Venn diagrams, differences table, lists, and so on.
Structures
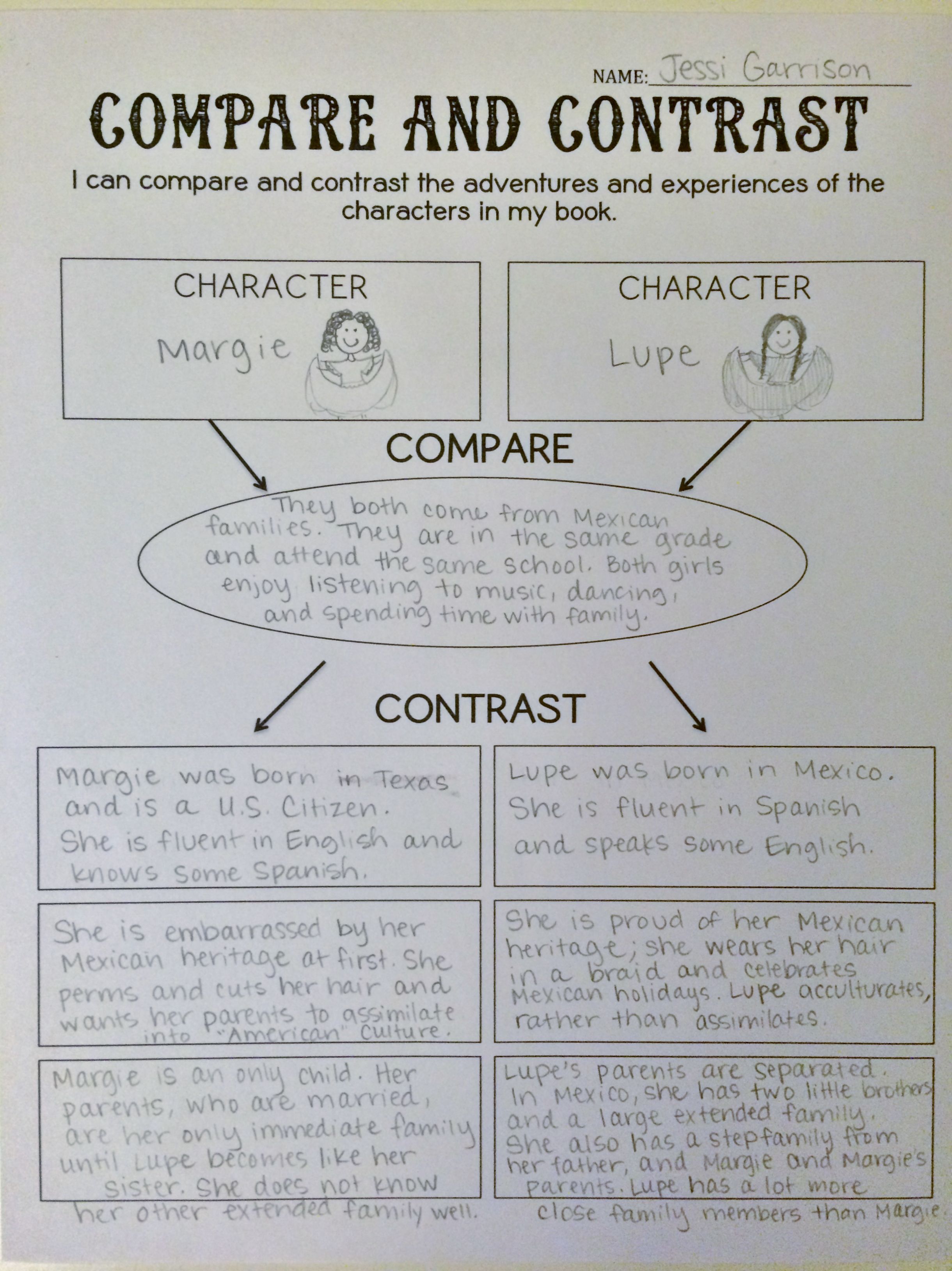
There are many ways to present your findings. My favorite is the list and the contrast table.
Lists
Here is an example of how I use lists.
Weight and mass are similar in multiple ways. They are both used in engineering and physics. They both appear in \(W = mg\). However, they also differ in significant ways. Here are some of those.
Meaning: Mass is a measure of how much matter a body has. Weight is the amount of gravitational force acting on body.
Location: The mass of a body is independent of location. A 6 kg object will have a mass of 6 kg anywhere in the universe. Weight depends on location. For example the weight of an object on earth is about six times larger than the weight of the same object on the moon.
Units. Weight has force units: newtons, pounds-force, dynes, and so on. Mass units are kilograms, pounds-mass, grams, and so forth.
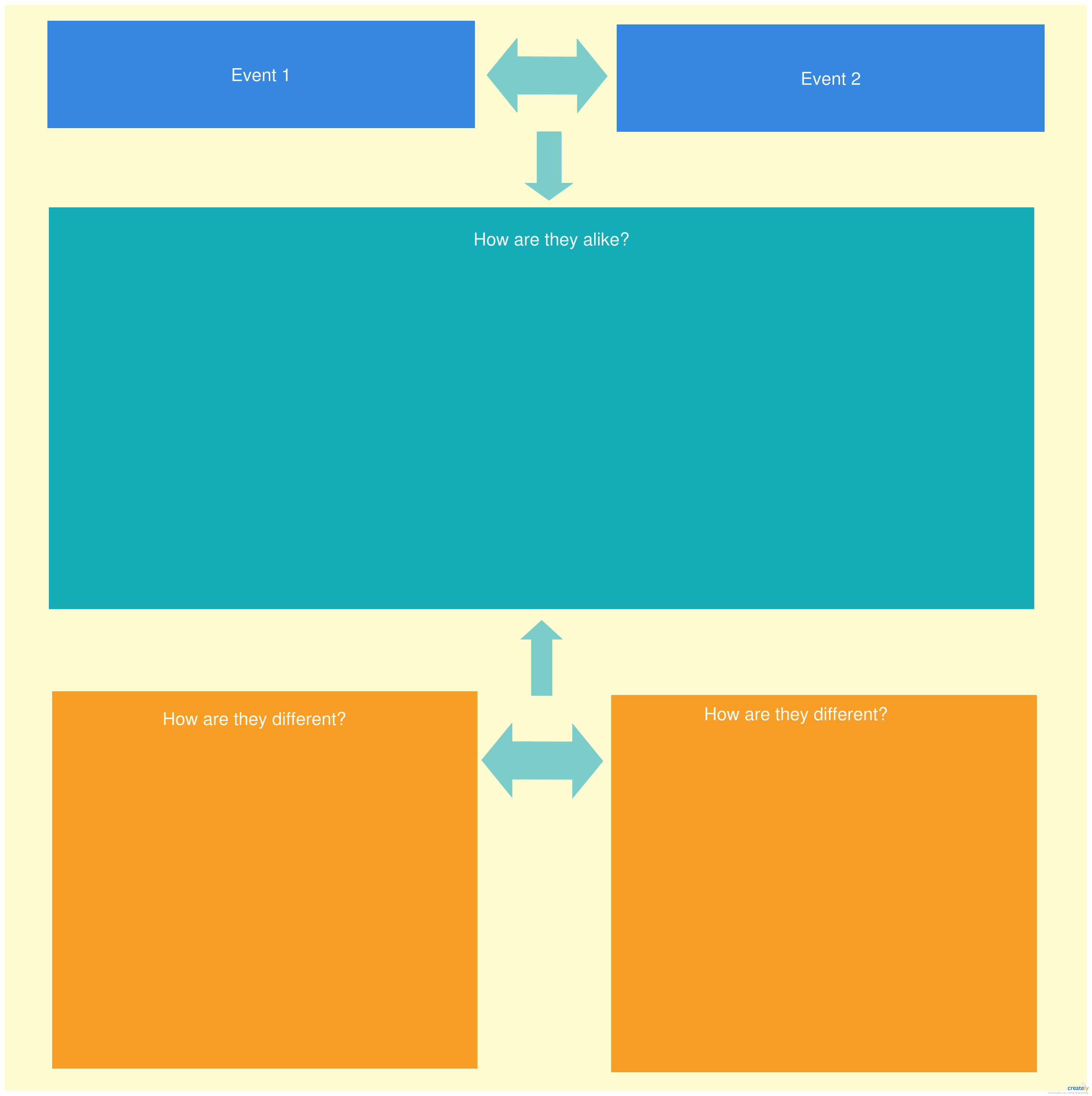
The generic structure for comparing A and B goes like this.
A and B are similar in several ways. List of similarities, typically using a run-in list structure. However, there are different in the following ways.
- Attribute 1: Describe how A and B are different.
- Attribute 1: Describe how A and B are different.
- Attribute 1: Describe how A and B are different.
Venn Diagram
Here is an example comparing bats and birds.
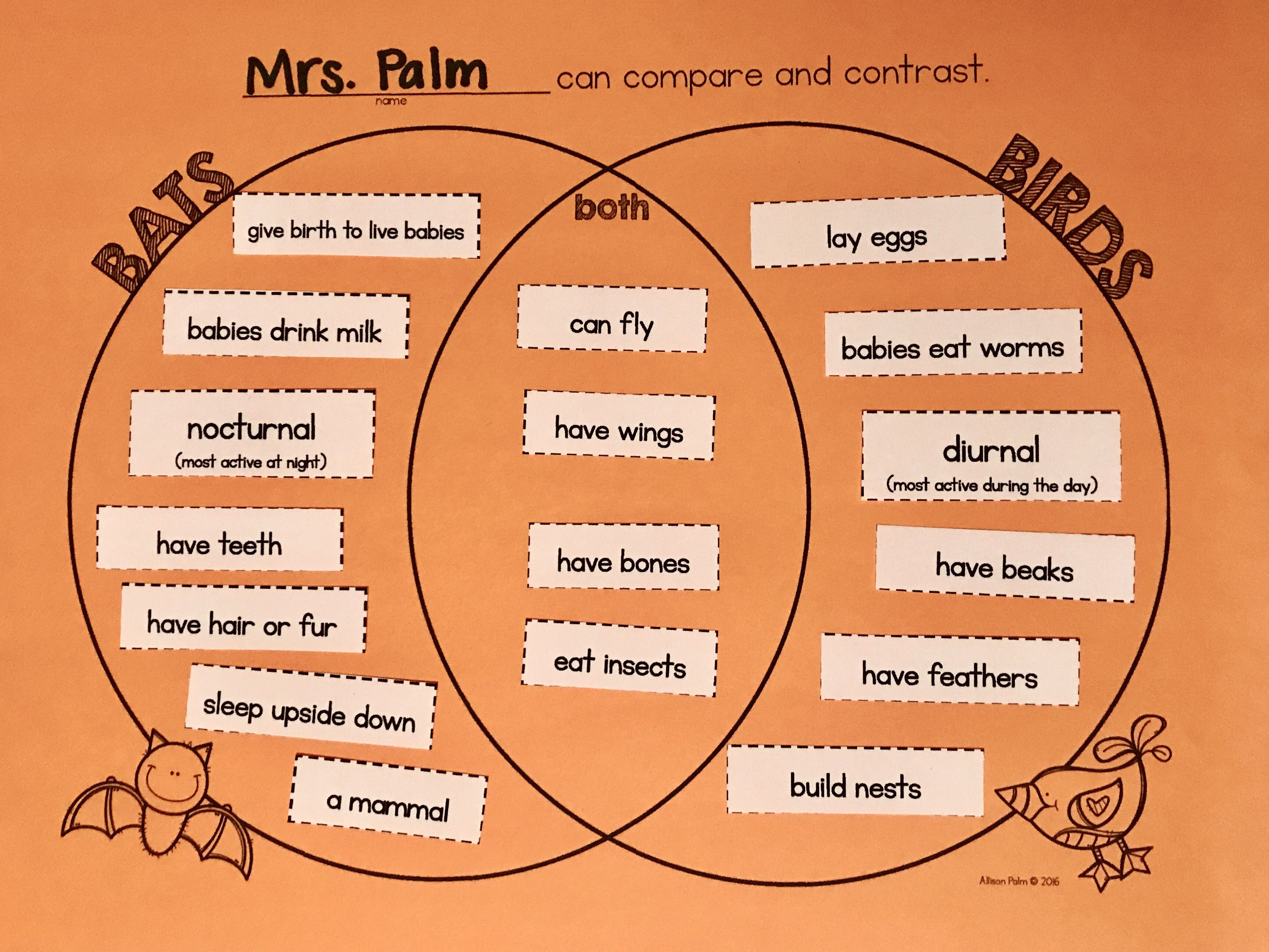 Here
is an image showing the generic structure
Here
is an image showing the generic structure
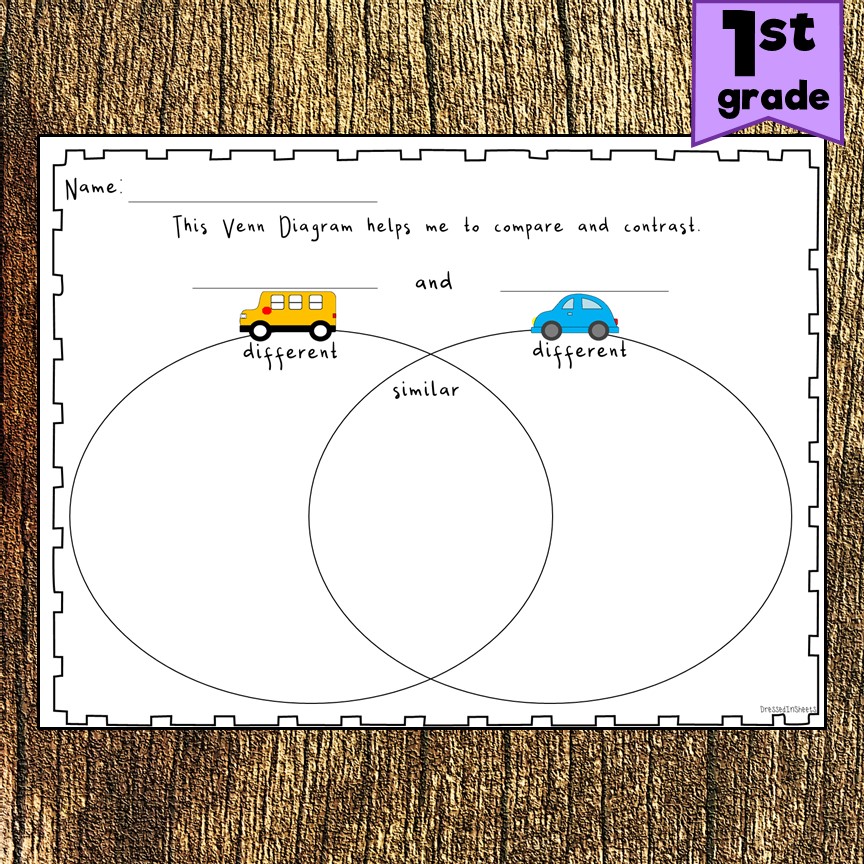 This next
image also illustrates the structure
This next
image also illustrates the structure
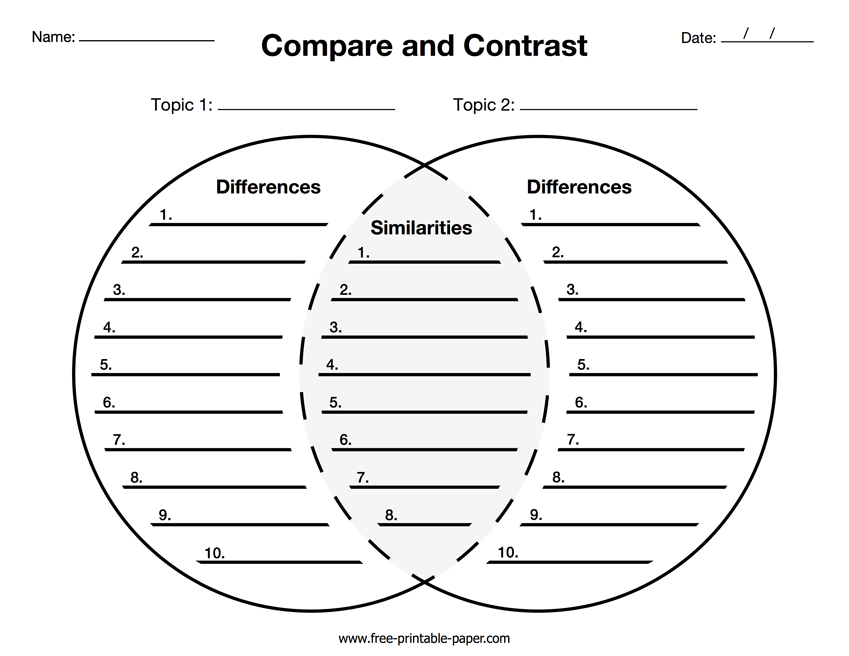 Venn
Diagram: A Venn diagram is a graphical representation of the
relationships between sets, using overlapping circles to show the
commonalities and differences between them.
Venn
Diagram: A Venn diagram is a graphical representation of the
relationships between sets, using overlapping circles to show the
commonalities and differences between them.
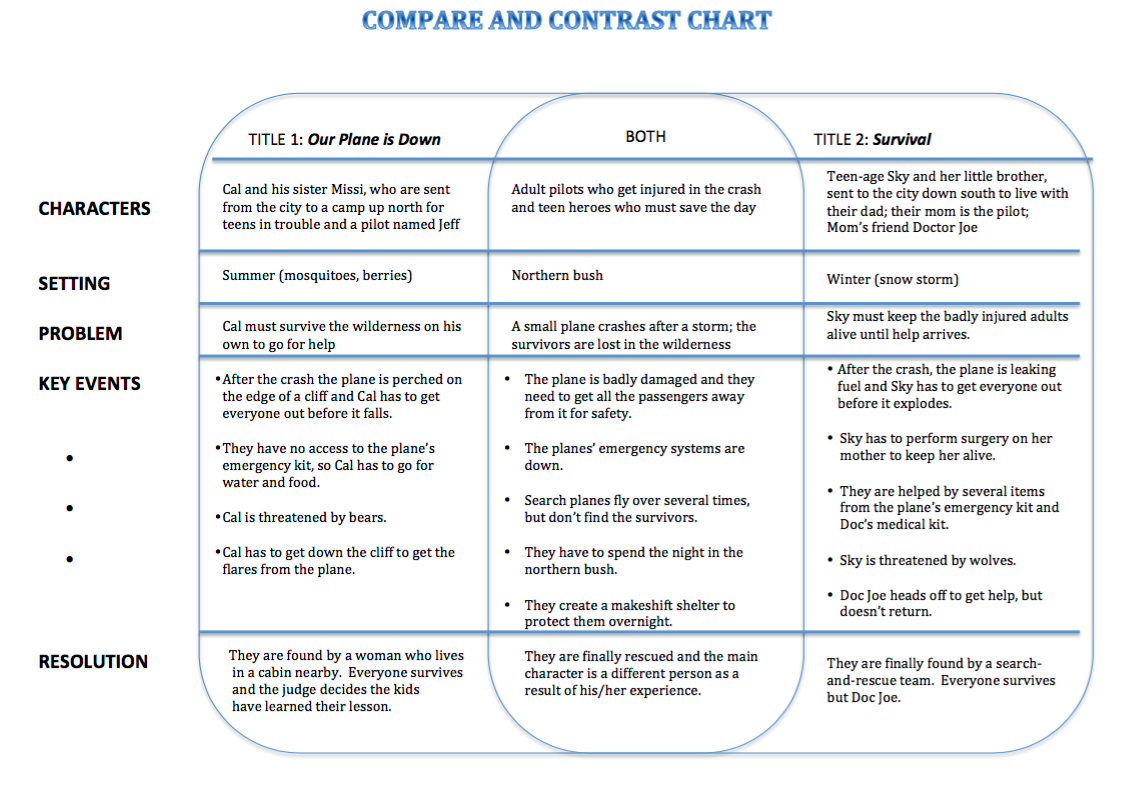
Contrast Table
Here is an example from statistics. Note. These tables are really
useful for learning abstract concepts.
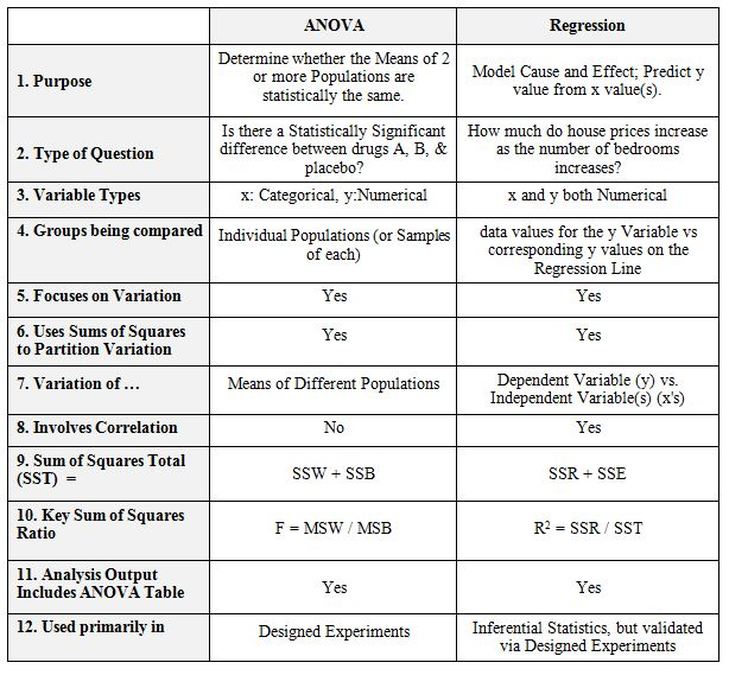 The next two
images illustrate the structure.
The next two
images illustrate the structure.
 ![[COMPARISON_CONTRAST_CHART_Page_1.webp]]
![[COMPARISON_CONTRAST_CHART_Page_1.webp]]
Other Structures
 ##
Rationale
##
Rationale
The “Compare and Contrast” skill is super useful for learning, teaching, decision making, explaining, understanding, and so forth
To understand better: Comparing and contrasting help individuals gain a clearer and more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter by highlighting its various facets.
To make informed decisions: It assists in decision-making by providing a basis for evaluating options and choosing the most suitable one.
To facilitate learning: In education, comparing and contrasting are often used as teaching tools to help students grasp complex concepts and develop critical thinking skills.
To solve problems: Analyzing similarities and differences can be instrumental in problem-solving, as it aids in identifying solutions or alternative approaches.
- How:
- Identify the subjects of comparison/contrast: Determine what you want to compare or contrast. This could be objects, ideas, concepts, individuals, etc.
- Establish criteria: Decide on the specific criteria or aspects you will focus on when making comparisons or contrasts. These criteria depend on the context and purpose.
- Gather information: Collect relevant information or data about each subject being compared or contrasted.
- Create a structure: Organize your comparison or contrast in a clear and logical manner, using methods such as lists, tables, Venn diagrams, or paragraphs.
- Analyze and interpret: Examine the collected information and draw conclusions about the similarities and differences.
- Provide evidence: Support your comparisons and contrasts with evidence or examples to make your analysis more convincing.
- When:
- Academically: Comparing and contrasting are commonly used in essays, research papers, and presentations to analyze literature, historical events, scientific theories, and more.
- Decision-making: When faced with choices, individuals often use this approach to weigh the pros and cons of different options.
- Problem-solving: It is employed to identify solutions or approaches to address issues or challenges.
- Critical thinking: As a mental exercise, comparing and contrasting can be practiced regularly to enhance one’s critical thinking skills.
In summary, comparing and contrasting are valuable tools for gaining insights, making decisions, solving problems, and developing critical thinking skills. They are used across various contexts to explore and analyze the similarities and differences between different subjects, leading to a deeper understanding and informed choices.