Circular Dependency
- id: 1699006796
- Date: June 8, 2024, 2:26 p.m.
- Author: Donald F. Elger
Synonym: Interdependent Relationship
An interdependent relationship refers to a situation where two or more entities rely on each other to function or exist.
Introduction
We all aspire to achieve outstanding outcomes in various aspects of life—whether it’s winning a championship, crafting and constructing our dream home, amassing significant wealth for financial independence, launching a successful startup, acquiring our dream car, conquering a towering mountain, penning an exceptional novel, or pursuing whatever inspires us.
The critical factor in attaining exceptional results lies in comprehending the underlying factors or catalysts that drive such achievements. However, even with a profound understanding, we may encounter challenges due to the presence of circular dependencies.
Thus, this lesson describe circular dependencies and how to apply this information to attain exceptional results.
What is a Circular Dependency?
A circular dependency refers to a situation in which two or more elements or components depend on each other in a loop, creating a self-reinforcing or interdependent relationship. In such cases, it can be challenging to determine a clear starting point or causal direction between the elements.
Visual Representation
A simple circular dependency is that we cannot have chickens without eggs and we cannot have eggs without chickens. Both components are mutually dependent on each other.
So we can make a diagram as shown below that shows the cause and effect of a circular dependency. The egg causes the chicken. The chicken causes the egg. Both are interdependent on one another.
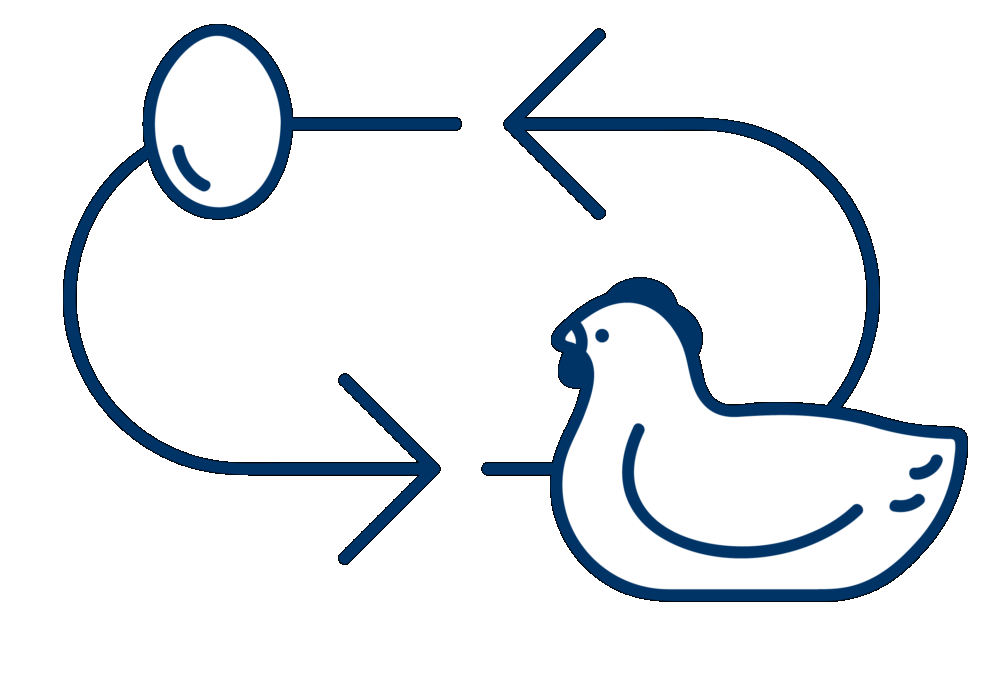 Image
from Breaking
Up Circular Dependencies | CB Insights Research
Image
from Breaking
Up Circular Dependencies | CB Insights Research
Examples of Circular Dependency
Great results for a company (healthy financials plus awesome products) cannot be built unless you have a great culture. A great culture cannot be created unless you have a great company.
Virtuoso cello playing cannot be attained unless a person does a great deal of learning as in years and years. Learning to play the cello skillfully cannot done unless the student has the vision of playing really well and this drives them to put in all the hours of practice.
In software development, Module A depends on Module B, and Module B depends on Module A, creating a code structure that is difficult to understand and maintain.
In finance, a company’s stock price depends on investor sentiment, and investor sentiment is influenced by the company’s stock price, leading to a feedback loop.
In personal relationships, trust depends on open communication, and open communication depends on trust, creating a cycle where both elements reinforce each other.
Why Circular Dependency Occurs
Circular dependencies can occur for various reasons, including mutual dependence, feedback loops, and a lack of a clear hierarchy of cause and effect.
How Circular Dependency Manifests
Circular dependency can manifest in different ways, such as code that’s hard to compile or debug in programming, market instability in economics, or communication breakdowns in relationships.
Who Is Affected by Circular Dependency
Circular dependencies can affect individuals, organizations, and systems across various domains, including software development, finance, psychology, and social dynamics.
When Circular Dependency Occurs
Circular dependencies can occur at any time when there is an interdependent relationship between elements. They may persist until efforts are made to break the cycle or mitigate its effects.
Where Circular Dependency Can Be Found
Circular dependencies can be found in different contexts, including software and programming, economics and financial markets, interpersonal relationships and psychology, and environmental systems and feedback loops.
How Much Circular Dependency Matters
The significance of circular dependency varies depending on the context. In some cases, it may have minor consequences, while in others, it can lead to major challenges or disruptions. Recognizing and addressing circular dependencies is often crucial for maintaining stability and effectiveness within systems or processes.
Achieving Insanely Great Results
Identification: Identifying circular dependencies is the key to unlocking results that seem too good to be true. To identify these dependencies, focus on areas where people often struggle to excel. These challenges encompass a wide range of aspects, such as building exceptional teams, cultivating fulfilling relationships, launching successful startups, mastering computer programming, attaining inner peace, elevating an average company to excellence, fostering collaboration within organizations, finding happiness, achieving a state of flow, and more. As you gain experience and practice, you’ll become adept at pinpointing circular dependencies that hinder remarkable outcomes, and you’ll learn how to rectify these issues effectively.
Aspirations: Start by clarifying your deepest aspirations. What is it that you genuinely desire, something you’d pursue if there were no limitations? Apply this aspiration-driven mindset both to your personal goals and your group endeavors.
Modeling: Delve into the root causes of great results. Utilize cause-and-effect diagrams to aid your exploration. Visualize and outline the circular dependencies you encounter. Simplicity is key in this step.
Action: Translate your newfound understanding, your model of the situation, into immediate actions you can take today. Continuously refine your model until it becomes a reliable map for turning your aspirations and dreams into reality.